Google Cartographer
System Overview
Google Cartographer provides a real-time solution for indoor mapping
in the form of a sensor-equipped backpack that generates 2D grid maps
with a
Laser scans are inserted into a submap at the best estimated position, which is assumed to be sufficiently accurate for short periods of time. Scan matching happens against a recent submap, so it only depends on recent scans, and the error of pose estimates in the world accumulates.
To cope with this accumulation of error, pose optimization is run regularly. When a submap is finished (i.e. no new scans are added in), it takes part in scan matching for loop closure. All finish submaps and scans are automatically considered for loop closure. If they are close enough based on current pose estimates, a scan matcher tries to find the scan in the submap, and if a good match is found within the currently estimated pose, it is added as a loop closing constraint to the optimization problem.
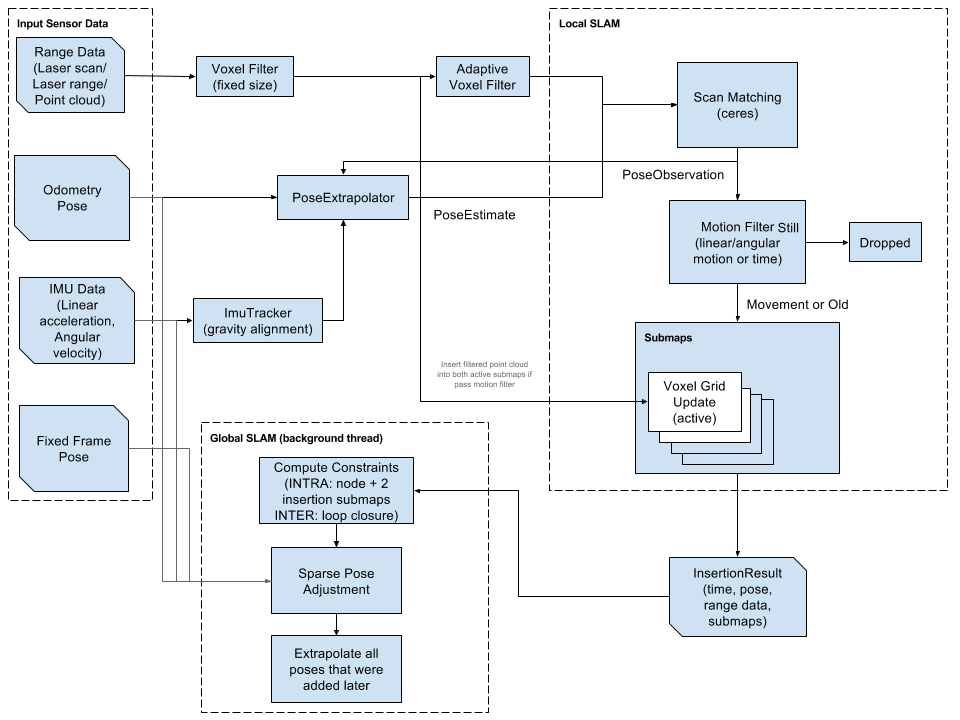
Bibliography
Hess, Wolfgang, Damon Kohler, Holger Rapp, and Daniel Andor. n.d. “Real-Time Loop Closure in 2D LIDAR SLAM.” In 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 1271–78.